What is Fasting and should you try it?
I’m hungry just thinking about it.
What is fasting?
Fasting has repeatedly been shown as beneficial for longevity
Fasting is a state of prolonged starvation in which your body draws on stored energy for fuel. After about one day your body turns to its stored carbohydrates called glycogen, for energy. After about two days when we have run through all our glycogen stores, our body begins to breakdown other sources of energy, including fats and protein.
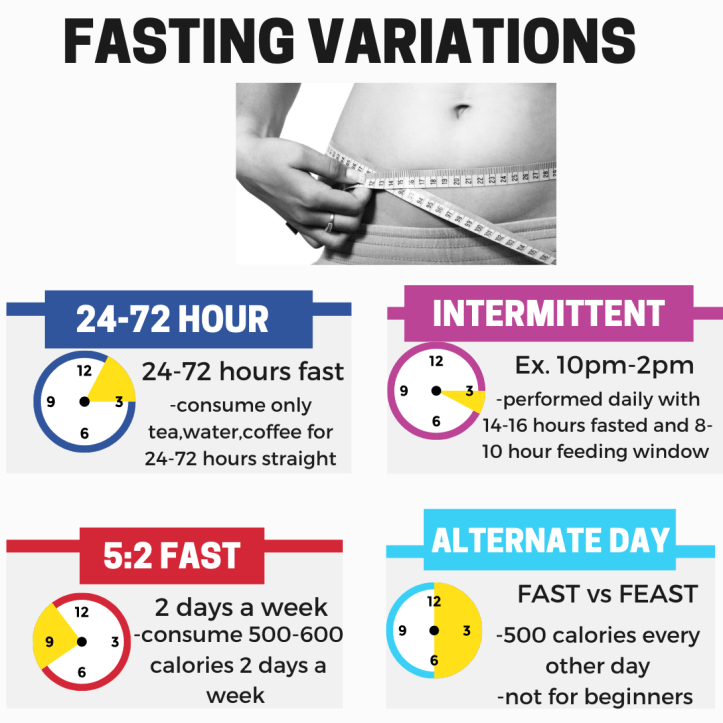
Types of fasting
How I implement fasting
I do my best to fast daily with an intermittent fast following 16 hours of fasting with 8 hours of feasting on gut friendly foods. Before I break my fast, I consume bone broth to prepare my gut for solid foods. Another Wheelthy fasting favorite is a 24-72 hour fast. The 24-72 hour fast is a favorite during times of gut distress. In order to maximize the gut healing effects of fasting I will incorporate bone broth into the fast as a meal replacement. I will also take gut friendly supplements such as probiotics, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D-3, chlorophyll, and spirulina. Within the 24-72 hours of fasting I will notice beneficial changes in my gut.
Fasting and the metabolic syndrome
potential to decrease belly fat, reduce blood pressure, treat obesity, lower prevalence of diabetes and improve glucose metabolism
The beneficial impact of periodic fasting and obesity is an area that has been well researched and documented. Fasting has been found to improve conditions associated with obesity including increasing the ability to lose belly fat, improve glucose metabolism and reduce hypertension, high blood pressure. Researchers believe fasting regimens have the potential to lower the prevalence of diabetes.
In one study, body fat and blood pressure were reduced, and glucose metabolism improved in obese subjects in response to an alternate day modified fast. In another study, for 6 months overweight subjects maintained a twice weekly intermittent fasting diet in which they consumed 500-600 calories on fasting days. This study saw a loss in abdominal fat and subjects displayed improved insulin sensitivity and reduced blood pressure. While the previous study was carried out over 6 months, a similar study saw similar results with only 3 weeks of alternate day fasting. These results included reduction in body fat and reduction in insulin levels in normal weight men and women.
Fasting and Exercise
When combined, fasting and exercise retard aging and disease
Fasting mimics exercise, proving to be useful for those wishing to gain the benefits of exercise but may be limited in the amount they can work. Fasting can also reduce stress and inflammation throughout the body and brain.
Fasting mimics physiological responses close to regular aerobic exercise. When combined, fasting and exercise retard aging and disease.
Fasting and cancer
Creates cell death to diseased or unhealthy cells
Fasting promotes autophagy or cell death, in which unhealthy cells are disposed of and their machinery is recycled. Fasting also causes cell death and atrophy due to major decrease in glucose, insulin, and IGF-1.
Fasting and neurodegeneration
improve cognition, memory, and mild cognitive impairment
Another proposed benefit of fasting is that it can increase brain health and function. One version of fasting known as calorie restriction (CR) has been shown to improve cognitive function (verbal memory) in overweight women and elderly subjects. Fasting has also been shown to improve mild cognitive impairment when maintained for one month on low glycemic diet.
Fasting and Inflammation
Long term fasting combined with a vegetarian diet provides beneficial effects in the treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis. Long term as well as alternate day fasting resulted in reduction in asthma and inflammation during a 2-month period.
Re-feeding following Fasting
Re-feeding following a fast is crucial to create new healthy cells
In order to focus on creating healthy cells after a fast, the refueling process must feed the growth of new healthy new cells. One of the best ways to create healthy cells is by following a low inflammatory diet.
The re-feeding process following a fast is a crucial next step to ensuring healthy cell growth. Fasting is followed by a period of abnormally high cellular proliferation driven by replenishment of growth factors during re-feeding. The health of the new cells created depends entirely on how you choose to feed them. When combined with carcinogens during re-feeding, cell growth is accompanied with pre-cancerous lesions in tissue including liver and colon. Pre-clinical studies suggest that fasting can increase efficiency of chemotherapy. Fasting with chemotherapy was shown to be highly and consistently effective in enhancing chemotherapy. Precautions should be taken as the type of fast and duration are important due to malnourishment.
Precautions and limitations of fasting
data found in animal studies not easily translated into human, more research is needed
Most evidence supporting fasting has been shown to be true in pre-clinical animal models, as opposed to clinical evidence in humans. This makes it hard to find evidence supporting that fasting reduces risk of cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic diseases such as Alzheimer’s in humans. One reason for this may be that those are diseases tend to plague elderly populations, and fasting is not recommended to this demographic as weight loss is already an issue with this population.
Fasting has various impacts on different individuals, with some individuals reporting detrimental effects that may be counterbalance its anti-aging effects. More research is needed to understand the mechanism of action behind fasting and the type of fasting that can maximize longevity effects.
Final Thoughts
Fasting promotes optimal health and reduces the risk of many chronic diseases, particularly for those who are overweight and sedentary. Animal studies document robust and repeatable effects of fasting on health indicators including greater insulin sensitivity, reduced blood pressure, reduced body fat, reduced inflammation Fasting has also been shown to battle disease and improve disorders such as heart attacks, diabetes, stroke, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease.
Check out the Gut Health and Bone broth articles to learn more about gut health. Or for a tailor made program including diet and fitness advice, contact via email cwheeler@wheelthy.com